|
|
|
|
Title: Horsepower Defined
Describing the Principle: Horsepower (hp) is considered a measure of work, more specifically, a measure of the work being done within a certain time. Because time is considered, horsepower involves the rate at which work is being done. Another way of saying this is that horsepower is concerned with how long it takes to do a certain amount of work.
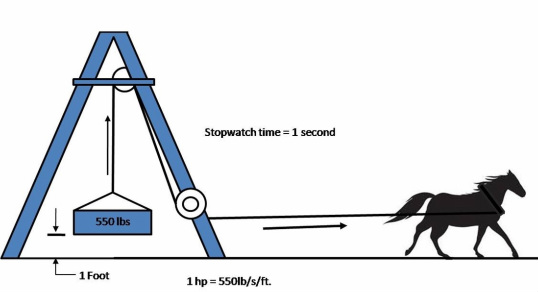
The classical definition of 1 horsepower is the amount of work needed to lift 550 pounds, 1 foot, in 1 second. This is graphically represented in the picture on above. It can also be said that in minutes, 1 horsepower is the amount of work needed to lift 33,000 pounds, 1 foot in 1 minute. These two definitions are the standard way of defining horsepower. Keep in mind that horsepower is applied in a straight line.
The work that comes out of the crankshaft of the engine is called torque, or twisting force. It is measured in foot pounds or often referred to as pound feet. The twisting forces are then sent through the drive train, through the differential and finally to the drive wheels of a vehicle. When the vehicle moves forward in a straight line, over a certain distance, within a certain time, horsepower is produce. This type of horsepower is called road horsepower.
Another type of horsepower is called brake horsepower. Brake horsepower (bhp) is defined as the actual horsepower at the rear of the engine under normal conditions. It is called brake horsepower because a brake is used to slow down (or load) the engine crankshaft inside a dynamometer. Since a dynamometer can only measure torque on an engine, brake horsepower is mathematically calculated using the following formula:
Brake horsepower = (torque x rpm) / 5,252
For example, if an engine were running at 3500 rpm and producing 350 foot pound of torque, under these condition, the engine would be able to produce 233 brake horsepower. (350 x 3500) / 5,252 = 233 bhp
Back to Mechanical Principles
Describing the Principle: Horsepower (hp) is considered a measure of work, more specifically, a measure of the work being done within a certain time. Because time is considered, horsepower involves the rate at which work is being done. Another way of saying this is that horsepower is concerned with how long it takes to do a certain amount of work.
The classical definition of 1 horsepower is the amount of work needed to lift 550 pounds, 1 foot, in 1 second. This is graphically represented in the picture on above. It can also be said that in minutes, 1 horsepower is the amount of work needed to lift 33,000 pounds, 1 foot in 1 minute. These two definitions are the standard way of defining horsepower. Keep in mind that horsepower is applied in a straight line.
The work that comes out of the crankshaft of the engine is called torque, or twisting force. It is measured in foot pounds or often referred to as pound feet. The twisting forces are then sent through the drive train, through the differential and finally to the drive wheels of a vehicle. When the vehicle moves forward in a straight line, over a certain distance, within a certain time, horsepower is produce. This type of horsepower is called road horsepower.
Another type of horsepower is called brake horsepower. Brake horsepower (bhp) is defined as the actual horsepower at the rear of the engine under normal conditions. It is called brake horsepower because a brake is used to slow down (or load) the engine crankshaft inside a dynamometer. Since a dynamometer can only measure torque on an engine, brake horsepower is mathematically calculated using the following formula:
Brake horsepower = (torque x rpm) / 5,252
For example, if an engine were running at 3500 rpm and producing 350 foot pound of torque, under these condition, the engine would be able to produce 233 brake horsepower. (350 x 3500) / 5,252 = 233 bhp
Back to Mechanical Principles
|
|
|
|